Telecommunication devices and computers use signals to represent data. These signals are transmitted from one device to another in the form of electromagnetic energy. Electromagnetic energy is a combination of electrical and magnetic fields vibrating in relation to each other. These signals can travel through a Vacuum, air or other transmission media.
Frequency: Electromagnetic spectrum extends in either direction. from the visible range. Radio waves are a form of electromagnetic radiation that results from oscillations of particles.
The number of oscillations per second refers to frequency and is measured in units of ‘hertz’ with kilohertz measuring thousands of hertz, megahertz measuring millions of hertz, & gigahertz measuring billions of hertz.
The fundamental relation between f, A. c (in vacuum) is
λf = C
Where c is a constant
To send and receive signals across the radio spectrum effectively, transmitters and receivers are designed to operate at particular frequencies.
The signal is a function of time, but it can be expressed as a function of frequency.
The signal consists of components of different frequencies.
It turns out that the frequency-domain view of a signal is important to an understanding of data transmission than a time-domain view. Both views are introduced here.
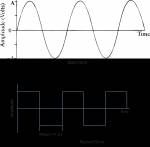
The time domain representation displays a signal using time-domain plot, which shows
changes in signal amplitude with time.
The relationship between amplitude and frequency is provided by frequency domain representation, which can be displayed with the help of spectrum analyser.