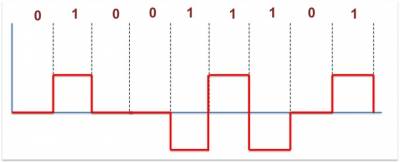
Bipolar Alternate Mark Inversion (AMI)
A simple bipolar encoding schemes is Alternate Mark Inversion (AMI).
The work MARK comes from telegraphy and it means 1. So AMI means alternate 1 inversion.
A variation of bipolar AMI is called pseudoternary.
It is the binary 1 that is represented by the absence of a line signal and the binary 0 by alternating positive and negative pulses.
A long string of O's in the case of AMI presents a problem of synchronization.
Several techniques have been used to address this deficiency.
One approach is to insert additional bits that force transitions.
Bipolar Alternate Mark Inversion (AMI)
This technique is used in ISDN for relatively low data rate transmission.
To cope with high signal transmission rate at high data rates, a technique that involves scrambling the data is used.
- -No D.C. component should be there.
- -Filling sequence should not result in long sequences of zero level.
- -Data transmission rate should not be reduces.
- -Filling sequences should have error detection capability.
Two commonly used scrambling techniques are B8ZS and HDB3.